By: Zoltan Buzady, Agnes Wimmer, Anita Csesznak & Peter Szentesi at Corvinus University of Budapest, Hungary
In: Interactive Learning Environments Scopus cite score: 7.2, (Q1)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2022.2098775
Abstract
The considerable proliferation of serious games (SG) in management education necessitates an academic foundation grounded in the concepts and practice of leadership, Flow, learning and development theory. Going beyond addressing the benefits of SG, this study is the first to demonstrate the successful use of SG in two areas: (a) teaching Flow theory within management studies via dedicated software designed to train a Flow-promoting Leadership style; and (b) showing that SG can serve as an innovative tool for measuring 29 leadership skills. The article demonstrates how non-intrusive data – collected during FLIGBY gameplay by 7931 managers globally, who made 150+ simulated leadership decisions – de facto support the process of leadership skill development. The findings show the system of relationships among the four critical Flow-promoting Leadership Skills that are needed for leading a work environment with more frequent Flow experiences. The results support educators and content developers in their quest to find optimal pathways and combinations for effectively developing skills by showing the underlying complexities of Flow and Leadership. The study contributes to the application of Flow-promoting leadership theory in practice via the help of innovative SG technology.
Keywords: serious games, game-based psychometrics, flow theory, leadership skills measurement, adaptive learning system
Contact Dr. Zoltan Buzady via email.
Summary and conclusions
We have demonstrated the concrete and effective application of serious gaming technology for the measurement and analysis of leadership skills, including the four that promote a greater Flow experience for employees at work. We show that, beyond the traditional methods of measuring leadership skills (primarily self-assessment via questionnaires and external rating via an assessor), a third method can be effectively used. The key scientific result of the work is the introduction of game-based psychometrics that can be used to effectively explore complex leadership skillsets and correlations thereof.
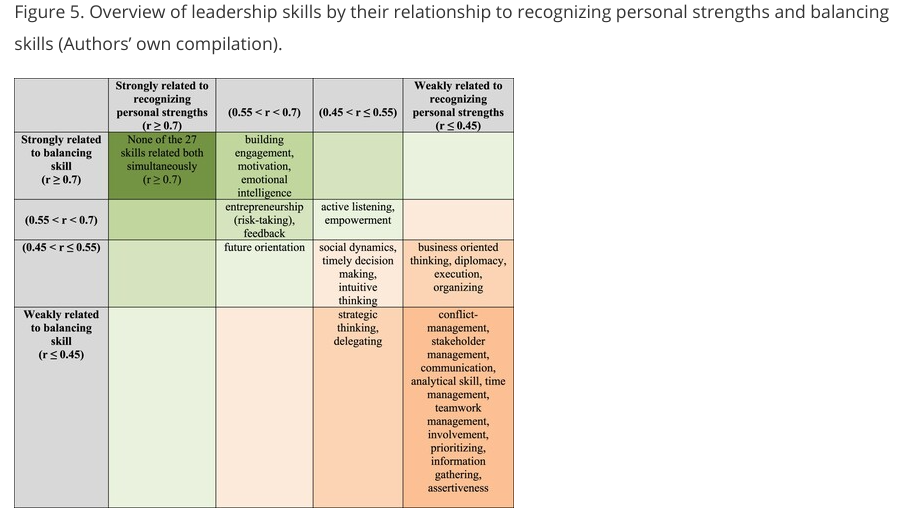
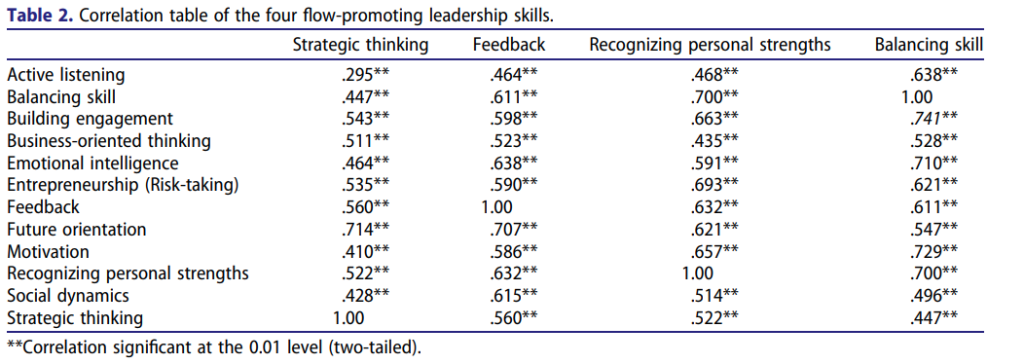
Virtual stories and decision dilemmas in serious games enable the unbiased, objective collection and reporting of data about gamer decisions. Expert coding and decoding of the underlying patterns of leadership skills and resulting leadership styles and preferences can be used to compare strengths and weaknesses with other players in the same cohort or across larger global populations. The four Flow-promoting leadership skills by Csikszentmihalyi have thus been more deeply explored and empirical support for their interrelatedness has been provided, and a further set of strongly associated leadership skills revealed.
The unique dataset contains the leadership skill scores of several thousand individuals from across the globe measured via FLIGBY®, a Flow-leadership development serious game. The strongest connection was revealed between the leadership skill of discovering a person’s personal strengths and the skill of creating the right balance between challenge and skill level. This confirms the hypothesis of Flow-promoting leadership theory: a leader should be aware of followers’ abilities and skills so as to better motivate them by assigning those tasks which are sufficiently challenging yet can be accomplished. The empirical analysis confirmed the researchers’ hypothesis and demonstrated a clear and strong connection between the four Flow-promoting leadership skills. Furthermore, the study revealed the most significant interconnections among the 29 leadership skills, and among these the core FPL skills.
LIST of Our Most Important Academic Publications HERE